Objective Comments and Analysis - All Science, No Politics
Primary Author Richard James
2010-2013 Author Rick Thoman
Friday, September 29, 2023
Brink of Winter
Monday, September 25, 2023
Getting Frosty
Wednesday, September 20, 2023
Subsea Cable Fixed
Friday, September 15, 2023
August Climate Data
Looking back at climate data for August, it was a very warm month indeed - the 3rd warmest on record for the state overall. Only in 1977 and 2004 was the month of August warmer for Alaska as a whole. It was also the warmest month of the 2023 summer relative to normal; there were only a few days in August that were marginally cooler than normal overall.
Regionally, the warmth was most unusual across the eastern interior, and southwestern Alaska was relatively cooler. A major trough-ridge contrast explains the pattern; both the trough over the Aleutians and the ridge over western Canada (and SE Alaska) were quite strong for the time of year, and the circulation anomaly pumped a great deal of warm air northward into Alaska.
South-central Alaska saw yet another wet and cloudy month, and the Southeast had more rain than in the very dry July, but it was still drier than normal. ERA5 and NCEI disagree on whether the Southeast Interior saw moisture relief, but Rick Thoman notes that rains were highly variable in that area; some places remained very dry.
The trend towards warmer conditions as summer progressed probably had at least some connection to the developing El Niño, because a ridge over southern and eastern Alaska, and northwestern Canada, is a typical feature when El Niño is occurring in August. The map below shows the typical August 500mb height patterns during El Niño.
However, other aspects of the circulation pattern from eastern Asia to Canada were highly atypical for El Niño. Notice the tendency for lower heights/pressure near the Sea of Japan: that's the opposite of what happened in August this year (see the first map in this post). Also, most of Canada tends to be cooler than normal in August during El Niño (first map below), but in fact it was very warm across Canada's northern tier, and the record fire season just kept on going. The heat over Japan and northern Canada was relentless this summer, and that certainly can't be pinned on El Niño.
A better explanation for the overall North Pacific - North America pattern is the ongoing negative PDO phase. It's very unusual indeed for a negative PDO to persist as El Niño emerges, but this year the PDO has remained entrenched in the negative phase; and the warmth to the east of Japan has a lot to do with that (i.e. the warm SSTs there correspond to a negative PDO).
Here's the spatial (air) temperature pattern for August when the PDO is negative. It doesn't line up with the warmth in the eastern Pacific this year, but otherwise it's not a bad match from Japan to northern Canada. Texas tends to be hot too - and they had a really awful summer.
Rounding out the Alaska climate maps for August, it was cloudier than normal once again for western Alaska and the northern Gulf coast. It was also relatively windy from the Bering Sea to the western and northern interior.
It's also interesting to note the very high humidity (dewpoint) for much of the state. This goes a long way to explaining the extremely high overnight temperatures and therefore also the remarkably delayed autumn foliage in the Fairbanks area.
For future reference, I'll include maps below for climatological summer, June through August. It was the second warmest summer on record for the North Slope, and third warmest for the eastern interior climate divisions, according to the NCEI data. 2004 still holds the summer temperature record by some margin for the state as a whole and for the west coast, interior, and North Slope, as well as the northeast Gulf and central and southern panhandle regions. 2019 was the warmest summer for south-central and southwestern Alaska.
Rainfall, wind, and cloudiness were all exceptionally high for the northern Gulf Coast and southwestern mainland, but Southeast had really quite a dry and sunny summer.
And finally, it's just interesting to note again the dramatic shift that took place in mid-July as the weather suddenly and belatedly turned very warm.
Wednesday, September 13, 2023
Slowly Cooling Off
Overnight temperatures are now finally dipping below freezing in colder spots around the interior - and it's about time. The coldest reports this morning came from the usual places:
Salcha RAWS 22°F
Circle Hot Springs 25°F
Chicken 25°F
Bettles saw its first freeze of the season, 28°F, which is very late: the record latest is September 16 in 1978.
The coldest temperature so far at Fairbanks airport is only 38°F, which ties with 1989 and 2007 for record highest up to this date.
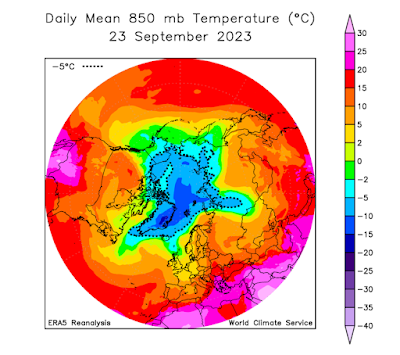
Astonishingly, it appears the autumn colors are *still* not fully developed around the Fairbanks area, although a change is starting to show up. Webcam views from Nenana and Cleary Summit today:
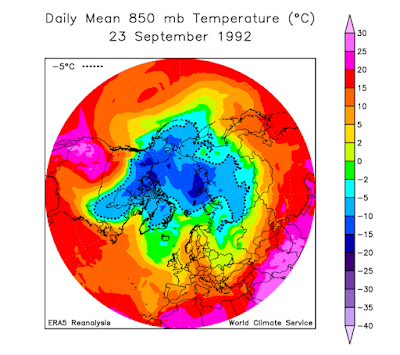
It's hard to believe that on this date in 1992, the permanent winter snow cover was established in Fairbanks. See the following write-up from Rick Thoman, with photos from this date 31 years ago!
https://ak-wx.blogspot.com/2013/09/septmeber-1992the-first-snows.html
Main blog entry here:
https://ak-wx.blogspot.com/2013/09/semptember-1992setting-table.html
Friday, September 8, 2023
Arctic Sea Ice Loss Revisited
An interesting study was published last week on the topic of Arctic sea ice loss, led by Igor Polyakov of UAF. Here's a write-up from the Geophysical Institute:
https://www.gi.alaska.edu/news/new-research-points-mechanisms-atlantification-arctic-ocean
The thrust of the paper is that a change in the Arctic atmospheric circulation has contributed to the lack of sea ice loss since 2007, when the seasonal minimum reached its first dramatic record low. Since then, Arctic sea ice has been relatively stable, and the new work suggests this is because the new wind patterns have been transporting more fresh water into the Pacific side of the basin. Fresh water is less dense than salt water and resides immediately under the sea ice, and it serves to insulate the ice from warmer ocean water that would otherwise tend to melt the ice from below.
The following figure from the paper shows the rather surprising hiatus in sea ice loss (based on September ice extent), and the inset map shows the change in upper ocean "available potential energy", which signifies the quantity of fresh water at the surface. The change to more fresh water and more stable conditions is largely found in the Beaufort and northern Chukchi Seas.
The paper presents a variety of oceanographic analyses to support the hypothesis about redistribution of fresh water into the Pacific sector, and the basic idea seems plausible to me. However, to throw in my own two cents, I also think it's likely that a portion of the fresh water volume increase has arisen because of greater precipitation and greater river inflows in the past 15 years.
Let's illustrate these two additional factors. First, it's well-known that the Arctic hydrological cycle is intensifying in response to rapid warming, and the 2021 NOAA Arctic Report Card highlighted the increase in Arctic river discharge, particularly for Eurasian rivers (providing the bulk of Arctic Ocean inflows):
Here's the link:
https://arctic.noaa.gov/report-card/report-card-2021/river-discharge/
The total discharge of all rivers to the Arctic Ocean is estimated to be approximately 5000 km3/year, which is equivalent to about 35 cm of fresh water depth over the entire Arctic Ocean area - but much of this water will reside close to the continents or be transported into the Pacific sector and the Beaufort Gyre, where salinity is low:
It seems plain that an increase in discharge will tend to fortify the fresh water layer in the Pacific/Canada sector of the ocean, especially with the more favorable wind circulation of recent years. The percentage change in river flows evidently isn't large, but the recent effect may have been magnified by the change in transport patterns. Here's a diagram of ocean and ice transport around the basin, from Polyakov et al:
The other factor may be increased precipitation. Ground-truth precipitation measurements are very scarce and uncertain, of course, so here's the ERA5 reanalysis estimate of annual precipitation change between the two 15-year periods that are compared in Polyakov et al.
An increase of 5-15% is widespread across the Asian side of the Arctic Ocean, according to the model. How much does this amount to? The annual mean precipitation is very low, only about 250-300 mm (10-12 inches) across much of the area where the increase has occurred:
But in the northern Barents Sea, where annual precipitation is higher and the percentage increase has been large, the absolute increase amounts to 50-100 mm/year.
Interestingly, the total Arctic Ocean fresh water input appears to be roughly evenly split between the average ~35cm depth of river discharge and the average precipitation of about 20-50 cm. (Some of the snow will evaporate, of course, but some of it melts in summer and feeds the surface fresh water layer.) With both fresh water sources producing higher volume in recent years, it seems this has probably contributed to the build-up of fresh water and thereby to the longevity of Arctic sea ice.
The question remaining in my mind is how long can sea ice melt be postponed by these mechanisms in the face of rapid atmospheric (and presumably ocean subsurface) warming? Polyakov et al suggest that the atmospheric circulation regime of the last 15 years is likely to reverse back to the opposite phase very soon, which would be unfavorable for sea ice and perhaps bring about another rapid decline. It does seem unlikely that sea ice will hold on much longer, unless something very unexpected happens. Courtesy of Zack Labe's website, Arctic temperatures are on a steep uptrend, including since 2007:
But time will tell, and I imagine that a few more surprises lie ahead.
Sunday, September 3, 2023
Record August Warmth
Just a quick note to re-emphasize how extraordinarily unusual the warmth of the last 6 weeks has been for the central and eastern interior, and particularly in terms of daily minimum temperatures.
Here's the leaderboard for average daily low temperatures in Fairbanks from July 16 through the end of August:
2023 55.2°F
2016 52.7°F
1990 52.5°F
2004 52.3°F
1974 52.3°F
2017 52.2°F
2021 52.0°F
This year stands out like a sore thumb. The departure from normal represents a 3.3 standard deviation anomaly compared to the 1991-2020 distribution. This is an extreme climate event, with a "return period" of many hundreds of years assuming a stable climate.
Accordingly, it's perhaps no surprise to see that there is *still* very little color in the foliage, based on Nenana and Cleary Summit webcam views from yesterday afternoon:
Here's a chart of Fairbanks airport daily minimum temperatures since June 1:
Looking at monthly statistics for August, Eagle had its warmest August on record (1905 is warmer in the books, but the minimum temperatures look much too high). Northway was also the warmest on record, while Fairbanks was 3rd warmest overall, but warmest for daily low temperatures. Gulkana also had its warmest August for daily low temperatures.
But change is in the air: snow was falling in the hills above Fairbanks yesterday morning. Here's a view from Wickersham Dome, before the sky cleared out later in the day.
Snow at 2600 feet north of Fairbanks this morning! @NWSFairbanks @Climatologist49 pic.twitter.com/pNCsUXk0YO
— Adam Gill (@adam_gillwx) September 2, 2023